Accounts receivable records transactions with customers who owe the business money. HighRadius’ Record to Report Solution significantly enhances the management of both temporary and permanent accounts by automating key processes and ensuring real-time accuracy. It streamlines the closing process for temporary accounts, accelerates financial reporting with real-time updates, and reduces manual errors through automated data entry and reconciliation. Inconsistent accounting practices can also lead to challenges in managing temporary and permanent accounts. It’s crucial to establish and maintain consistent accounting practices to ensure accurate financial reporting. Consistency in accounting practices helps businesses to track financial transactions accurately, identify discrepancies, and make informed decisions.
What are Permanent Accounts?
For example, your year-end inventory balance carries over into the new year and becomes your beginning inventory balance. Each time you make a purchase or sale, which of the following accounts are permanent you need to record the transaction using the correct account. Then, you can look at your accounts to get a snapshot of your company’s financial health.
Income summary accounts
Goodwill accounts represent the excess of the purchase price over the fair value of the identifiable assets of a business. The balance of these accounts decreases over time due to impairment. The three major accounting elements are assets, liabilities, and equity. Liabilities are debts or obligations that a business owes to others.
Examples of temporary and permanent accounts
- Whether you’re just starting your business or you’re already well on your way, keeping organized financial records is a must.
- Permanent accounts carry the ending balances of the balance sheet to the beginning of the next year.
- They track the money that a business earns from selling goods or services, as well as any other sources of income such as earned interest.
- To determine if an account is permanent or temporary, check if it carries its balance over to the next period.
- It is important for businesses to keep accurate records of their expenses in order to properly manage their finances and make informed decisions.
Unlike temporary accounts, you do not need to worry about closing out permanent accounts at the end of the period. Instead, your permanent accounts will track funds for multiple fiscal periods from year to year. Income summary effectively collects NI for the period and distributes the amount to be retained into retained earnings.
FAR CPA Practice Questions: Capital Account Activity in Pass-through Entities
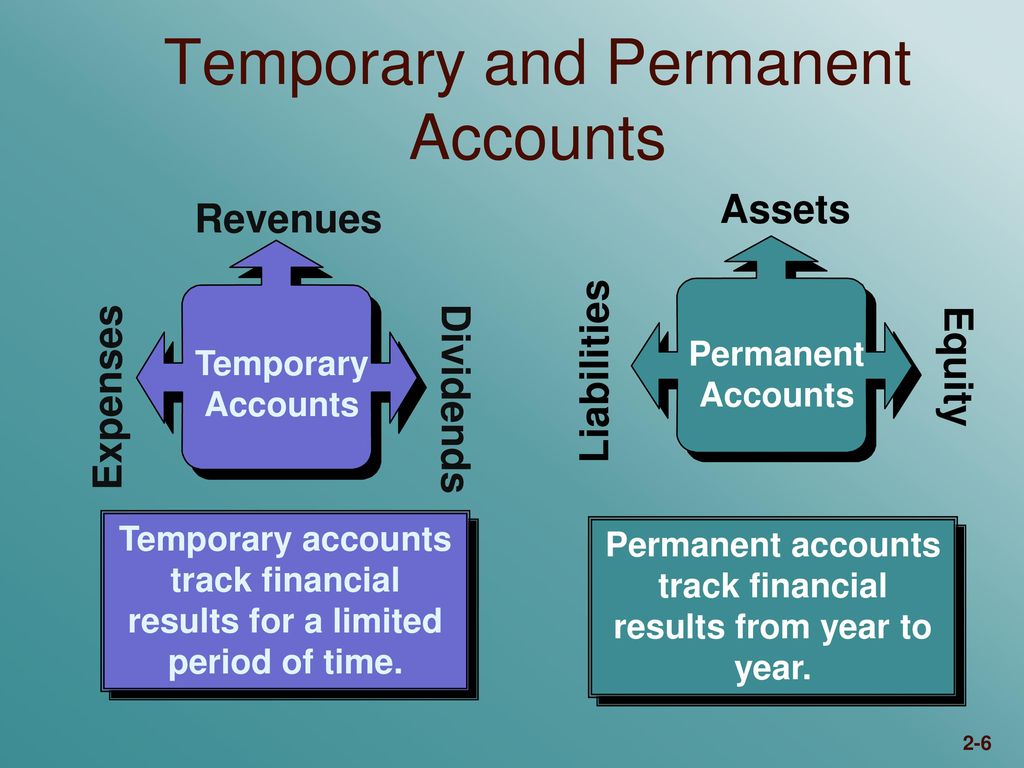
They are closed at the end of every year so as not to be mixed with the income and expenses of the next periods. This way, users would be able know how much income was generated in 2019, 2020, 2021, and so on. Temporary accounts are closed into capital at the end of the accounting period. Real accounts are those that represent tangible or intangible assets of a business.
Company
This allows them to generate reports that show the financial performance of the company over time. Some common examples of revenue accounts include sales revenue, service revenue, and interest income. Sales revenue is the income generated from selling goods or products, while service revenue is the income generated from providing services to customers. Liability accounts are a type of account in which a company records its debts or obligations. These accounts are used to track the company’s financial obligations to its creditors, such as suppliers, lenders, and other entities.
At the closing stage of the accounting cycle, the balances in revenue accounts are credited and the balances in expense accounts are debited to the income and summary account. The net balance in the income and summary account and the balance in dividends paid account are carried to the retained earnings account. This results in zero balances in all revenue accounts, all expense accounts, the income and expense summary account, and the dividends paid account.
Examples include rent expense, which records costs related to office or retail space, and salary expense, which captures employee wages. These accounts are closed at period end and their balances are transferred to the income summary account. Real accounts are accounts that represent tangible assets, such as property, plant, and equipment. Real accounts are also known as permanent accounts because they are not closed at the end of each accounting period. Real accounts are used to track the changes in the value of assets over time. The balance of real accounts is carried forward to the next accounting period.
